Risk governance
ADIB employs a robust credit and investment approval system and implements the Basel III Standardised approach for managing credit risk. The bank’s objectives are to minimise its risk profile while maintaining a strong performance and to be resilient and self-reliant under unforeseeable adverse events.
To that end, the Bank has a suite of internal policies addressing credit risk, investment risk, and defining risk appetite.
Effective risk management is a critical part of the ADIB corporate governance framework. Responsibility for setting ADIB’s risk appetite and for the effective management of principal risks rests with the Board. For more information about risk governance, please view our cooperate governance report on page 54 of the
2022 annual report.
ADIB aims to review its risk management framework to incorporate ESG risks that can translate into credit risk. Hence, ADIB aims to incorporate ESG risk assessment within the risk management process. In alignment with the Basel committee guidelines on the integration of ESG factors into banking supervision and regulation, ADIB aims to present a clear strategy and governance structure in place to integrate ESG factors into the Bank’s Risk Governance Framework; Identify, assess, and manage the risks associated with ESG factors in a comprehensive and systematic manner; conduct scenario analysis to assess the potential impact of ESG risks on the Bank’s balance sheet and business operations.
A focus on climate related risks
Climate change and environmental degradation are sources of structural change that affect economic activity, and consequently the financial system. Such risks are understood to potentially impact a bank through degradation of its risk profile in relation to Credit, Market, Liquidity or Operational risk, as well as Reputation or Legal risks.
ADIB is exposed to ESG risks, like the rest of the financial services industry, through its transactions with clients and counterparties including corporates, households, sovereigns, and other financial institutions.
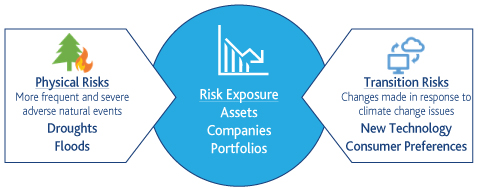
ADIB strives to integrate Climate change risks in the Bank’s credit policy and procedures. The principal risk drivers of climate change risks are:
-
Physical risk: refers to the financial impact of a changing climate, including more frequent extreme weather events and gradual changes in climate, as well as of environmental degradation, such as air, water and land pollution, water stress, biodiversity loss and deforestation. This can directly result in, for example, damage to property or reduced productivity, or indirectly lead to subsequent event, such as the disruption of supply chains.
-
Transition risk: refers to an institution’s financial loss that can result, directly or indirectly, from the process of adjustment towards a lower-carbon and more environmentally sustainable economy. This could be triggered, for example, by a relatively abrupt adoption of climate and environmental policies, technological policies, technological progress or changes in market sentiment and preferences.
Scenario analysis and stress testing
ADIB commits to explore the impacts of climate change and the transition to a low-carbon economy on the Bank’s strategy and the resiliency of its business model through identifying relevant climate-related risk; measuring vulnerability to climate-related risks and estimating exposures and potential losses; diagnosing data and methodological limitations in climate risk management; and informing the adequacy of the Bank’s Risk Governance Framework, including risk mitigation options.
ADIB will review the potential of regularly stress testing the bank’s operations and systems to identify and manage potential ESG risks and shocks including climate change risks. The Bank’s commitment to stress testing ESG factors will include conducting assessments of the Bank’s ESG risks and vulnerabilities, including climate change, social impact, and governance issues.
ADIB understands that stress testing ESG factors is an ongoing process that requires ongoing commitment and resources. We are committed to integrating ESG considerations into the Bank’s business strategy and operations to ensure the long-term success of our business and contribute to a sustainable future for all.
Integration of ESG factors in financing and investment activities
ESG due diligence is an important process for ADIB to assess and manage ESG risks and opportunities associated with the Bank’s financing and investment activities. ESG due diligence involves evaluating the potential impact of a borrower or investment on key ESG criteria and is supported with a three line of defense approach to ESG risk management.

Financing Exclusions
ADIB believes that considering ESG factors in the financing and investment decisions and in alignment with Islamic principles will support the Bank in hedging ESG related risks. ADIB excludes certain sectors from its portfolio and any industry that is deemed forbidden by the Sharia’a rulings and the UAE regulation.
- Alcohol (brewers, distillers & vintners, packagers, transporters, sellers and resellers)
- Tobacco
- Pork-related products (food products, food retailers & wholesalers, hotels, restaurants & bars)
- Conventional financial services (banking, insurance, investment services, insurance brokers, mortgage finance, etc.)
- Weapons and defense (defense industries, manufacturers of weapons, contractors, suppliers of offensive components and systems)
- Entertainment (hotels, casinos/gambling, cinema, pornography, music, etc.)
ADIB also excludes the following sectors from its financing and investment activities:
- Coal
- GMOs
- Genetic cloning
- Deforestation